Redis is a widely popular open-source high-performance in-memory data structure server, and a great companion to PostgreSQL. Redis in Pigsty is a production-ready complete solution supporting master-slave replication, sentinel high availability, and native cluster mode, with integrated monitoring and logging capabilities, along with automated installation, configuration, and operation playbooks.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Module: REDIS
- 1: Configuration
- 2: Parameters
- 3: Playbook
- 4: Administration
- 5: Monitoring
- 6: Metrics
- 7: FAQ
1 - Configuration
Concept
The entity model of Redis is almost the same as that of PostgreSQL, which also includes the concepts of Cluster and Instance. Note that the Cluster here does not refer to the native Redis Cluster mode.
The core difference between the REDIS module and the PGSQL module is that Redis uses a single-node multi-instance deployment rather than the 1:1 deployment: multiple Redis instances are typically deployed on a physical/virtual machine node to utilize multi-core CPUs fully. Therefore, the ways to configure and administer Redis instances are slightly different from PGSQL.
In Redis managed by Pigsty, nodes are entirely subordinate to the cluster, which means that currently, it is not allowed to deploy Redis instances of two different clusters on one node. However, this does not affect deploying multiple independent Redis primary-replica instances on one node. Of course, there are some limitations; for example, in this case, you cannot specify different passwords for different instances on the same node.
Identity Parameters
Redis identity parameters are required parameters when defining a Redis cluster.
| Name | Attribute | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
redis_cluster | REQUIRED, cluster level | Cluster name | redis-test |
redis_node | REQUIRED, node level | Node sequence number | 1,2 |
redis_instances | REQUIRED, node level | Instance definition | { 6001 : {} ,6002 : {}} |
redis_cluster: Redis cluster name, serves as the top-level namespace for cluster resources.redis_node: Redis node number, an integer unique within the cluster to distinguish different nodes.redis_instances: JSON object where keys are instance port numbers and values are JSON objects containing other instance configurations.
Redis Mode
There are three different working modes for Redis, specified by the redis_mode parameter:
standalone: Default standalone master-slave modecluster: Redis native distributed cluster modesentinel: Sentinel mode, providing high availability for standalone master-slave Redis
Here are three examples of Redis cluster definitions:
- A 1-node, one master & one slave Redis Standalone cluster:
redis-ms - A 1-node, 3-instance Redis Sentinel cluster:
redis-sentinel - A 2-node, 6-instance Redis Cluster:
redis-cluster
redis-ms: # redis classic primary & replica
hosts: { 10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } } }
vars: { redis_cluster: redis-ms ,redis_password: 'redis.ms' ,redis_max_memory: 64MB }
redis-meta: # redis sentinel x 3
hosts: { 10.10.10.11: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 26379: { } ,26380: { } ,26381: { } } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-meta
redis_password: 'redis.meta'
redis_mode: sentinel
redis_max_memory: 16MB
redis_sentinel_monitor: # primary list for redis sentinel, use cls as name, primary ip:port
- { name: redis-ms, host: 10.10.10.10, port: 6379 ,password: redis.ms, quorum: 2 }
redis-test: # redis native cluster: 3m x 3s
hosts:
10.10.10.12: { redis_node: 1 ,redis_instances: { 6379: { } ,6380: { } ,6381: { } } }
10.10.10.13: { redis_node: 2 ,redis_instances: { 6379: { } ,6380: { } ,6381: { } } }
vars: { redis_cluster: redis-test ,redis_password: 'redis.test' ,redis_mode: cluster, redis_max_memory: 32MB }
Limitations
- A Redis node can only belong to one Redis cluster, which means you cannot assign a node to two different Redis clusters simultaneously.
- On each Redis node, you need to assign a unique port number to each Redis instance to avoid port conflicts.
- Typically, the same Redis cluster will use the same password, but multiple Redis instances on a Redis node cannot have different passwords (because redis_exporter only allows one password).
- Redis Cluster has built-in HA, while standalone master-slave HA requires additional manual configuration in Sentinel since we don’t know if you have deployed Sentinel.
- Fortunately, configuring HA for standalone Redis is straightforward through Sentinel. For details, see Administration - Configure HA with Sentinel.
Typical Configuration Examples
Here are some common Redis configuration examples for different scenarios:
Cache Cluster (Pure In-Memory)
For pure caching scenarios with no data persistence requirements:
redis-cache:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { } } }
10.10.10.11: { redis_node: 2 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-cache
redis_password: 'cache.password'
redis_max_memory: 2GB
redis_mem_policy: allkeys-lru # evict LRU keys when memory is full
redis_rdb_save: [] # disable RDB persistence
redis_aof_enabled: false # disable AOF persistence
Session Store Cluster
For web application session storage with some persistence needs:
redis-session:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-session
redis_password: 'session.password'
redis_max_memory: 1GB
redis_mem_policy: volatile-lru # only evict keys with expire set
redis_rdb_save: ['300 1'] # save every 5 minutes if at least 1 change
redis_aof_enabled: false
Message Queue Cluster
For simple message queue scenarios requiring higher data reliability:
redis-queue:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-queue
redis_password: 'queue.password'
redis_max_memory: 4GB
redis_mem_policy: noeviction # reject writes when memory full, don't evict
redis_rdb_save: ['60 1'] # save every minute if at least 1 change
redis_aof_enabled: true # enable AOF for better persistence
High Availability Master-Slave Cluster
Master-slave cluster with Sentinel automatic failover:
# Master-slave cluster
redis-ha:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { } } } # primary
10.10.10.11: { redis_node: 2 , redis_instances: { 6379: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } } # replica 1
10.10.10.12: { redis_node: 3 , redis_instances: { 6379: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } } # replica 2
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-ha
redis_password: 'ha.password'
redis_max_memory: 8GB
# Sentinel cluster (manages the above master-slave cluster)
redis-sentinel:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 26379: { } } }
10.10.10.11: { redis_node: 2 , redis_instances: { 26379: { } } }
10.10.10.12: { redis_node: 3 , redis_instances: { 26379: { } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-sentinel
redis_password: 'sentinel.password'
redis_mode: sentinel
redis_max_memory: 64MB
redis_sentinel_monitor:
- { name: redis-ha, host: 10.10.10.10, port: 6379, password: 'ha.password', quorum: 2 }
Large-Scale Native Cluster
For high-volume, high-throughput scenarios using native distributed cluster:
redis-cluster:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { }, 6381: { } } }
10.10.10.11: { redis_node: 2 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { }, 6381: { } } }
10.10.10.12: { redis_node: 3 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { }, 6381: { } } }
10.10.10.13: { redis_node: 4 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { }, 6381: { } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-cluster
redis_password: 'cluster.password'
redis_mode: cluster
redis_cluster_replicas: 1 # 1 replica per primary shard
redis_max_memory: 16GB # max memory per instance
redis_rdb_save: ['900 1']
redis_aof_enabled: false
# This creates a 6-primary, 6-replica native cluster
# Total capacity ~96GB (6 * 16GB)
Security Hardening Configuration
Recommended security configuration for production environments:
redis-secure:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { } } }
vars:
redis_cluster: redis-secure
redis_password: 'StrongP@ssw0rd!' # use strong password
redis_bind_address: '' # bind to internal IP instead of 0.0.0.0
redis_max_memory: 4GB
redis_rename_commands: # rename dangerous commands
FLUSHDB: 'DANGEROUS_FLUSHDB'
FLUSHALL: 'DANGEROUS_FLUSHALL'
DEBUG: '' # disable command
CONFIG: 'ADMIN_CONFIG'
2 - Parameters
Parameter list for the REDIS module.
Parameter Overview
The REDIS parameter group is used for Redis cluster deployment and configuration, including identity, instance definitions, operating mode, memory configuration, persistence, and monitoring.
| Parameter | Type | Level | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
redis_cluster | string | C | Redis cluster name, required identity parameter |
redis_instances | dict | I | Redis instance definitions on this node |
redis_node | int | I | Redis node number, unique positive integer in cluster |
redis_fs_main | path | C | Redis main data directory, /data by default |
redis_exporter_enabled | bool | C | Enable Redis Exporter? |
redis_exporter_port | port | C | Redis Exporter listen port |
redis_exporter_options | string | C/I | Redis Exporter CLI arguments |
redis_mode | enum | C | Redis mode: standalone, cluster, sentinel |
redis_conf | string | C | Redis config template, except sentinel |
redis_bind_address | ip | C | Redis bind address, empty uses host IP |
redis_max_memory | size | C/I | Max memory for each Redis instance |
redis_mem_policy | enum | C | Redis memory eviction policy |
redis_password | password | C | Redis password, empty disables password |
redis_rdb_save | string[] | C | Redis RDB save directives, empty list disables RDB |
redis_aof_enabled | bool | C | Enable Redis AOF? |
redis_rename_commands | dict | C | Rename dangerous Redis commands |
redis_cluster_replicas | int | C | Replicas per master in Redis native cluster |
redis_sentinel_monitor | master[] | C | Master list for Redis Sentinel to monitor |
The REDIS_REMOVE parameter group controls Redis instance removal behavior.
| Parameter | Type | Level | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
redis_safeguard | bool | G/C/A | Prevent removing running Redis instances? |
redis_rm_data | bool | G/C/A | Remove Redis data directory when removing? |
redis_rm_pkg | bool | G/C/A | Uninstall Redis packages when removing? |
The Redis module contains 18 deployment parameters and 3 removal parameters.
#redis_cluster: <CLUSTER> # Redis cluster name, required identity parameter
#redis_node: 1 <NODE> # Redis node number, unique in cluster
#redis_instances: {} <NODE> # Redis instance definitions on this node
redis_fs_main: /data # Redis main data directory, `/data` by default
redis_exporter_enabled: true # Enable Redis Exporter?
redis_exporter_port: 9121 # Redis Exporter listen port
redis_exporter_options: '' # Redis Exporter CLI arguments
redis_mode: standalone # Redis mode: standalone, cluster, sentinel
redis_conf: redis.conf # Redis config template, except sentinel
redis_bind_address: '0.0.0.0' # Redis bind address, empty uses host IP
redis_max_memory: 1GB # Max memory for each Redis instance
redis_mem_policy: allkeys-lru # Redis memory eviction policy
redis_password: '' # Redis password, empty disables password
redis_rdb_save: ['1200 1'] # Redis RDB save directives, empty disables RDB
redis_aof_enabled: false # Enable Redis AOF?
redis_rename_commands: {} # Rename dangerous Redis commands
redis_cluster_replicas: 1 # Replicas per master in Redis native cluster
redis_sentinel_monitor: [] # Master list for Sentinel, sentinel mode only
# REDIS_REMOVE
redis_safeguard: false # Prevent removing running Redis instances?
redis_rm_data: true # Remove Redis data directory when removing?
redis_rm_pkg: false # Uninstall Redis packages when removing?
redis_cluster
Parameter: redis_cluster, Type: string, Level: C
Redis cluster name, a required identity parameter that must be explicitly configured at the cluster level. It serves as the namespace for resources within the cluster.
Must follow the naming pattern [a-z][a-z0-9-]* to comply with various identity constraints. Using redis- as a cluster name prefix is recommended.
redis_node
Parameter: redis_node, Type: int, Level: I
Redis node sequence number, a required identity parameter that must be explicitly configured at the node (Host) level.
A positive integer that should be unique within the cluster, used to distinguish and identify different nodes. Assign starting from 0 or 1.
redis_instances
Parameter: redis_instances, Type: dict, Level: I
Redis instance definitions on the current node, a required parameter that must be explicitly configured at the node (Host) level.
Format is a JSON key-value object where keys are numeric port numbers and values are instance-specific JSON configuration items.
redis-test: # redis native cluster: 3m x 3s
hosts:
10.10.10.12: { redis_node: 1 ,redis_instances: { 6379: { } ,6380: { } ,6381: { } } }
10.10.10.13: { redis_node: 2 ,redis_instances: { 6379: { } ,6380: { } ,6381: { } } }
vars: { redis_cluster: redis-test ,redis_password: 'redis.test' ,redis_mode: cluster, redis_max_memory: 32MB }
Each Redis instance listens on a unique port on its node. The replica_of field in instance configuration sets the upstream master address to establish replication:
redis_instances:
6379: {}
6380: { replica_of: '10.10.10.13 6379' }
6381: { replica_of: '10.10.10.13 6379' }
redis_fs_main
Parameter: redis_fs_main, Type: path, Level: C
Main data disk mount point for Redis, default is /data. Pigsty creates a redis directory under this path to store Redis data.
The actual data storage directory is /data/redis, owned by the redis OS user. See FHS: Redis for internal structure details.
redis_exporter_enabled
Parameter: redis_exporter_enabled, Type: bool, Level: C
Enable Redis Exporter monitoring component?
Enabled by default, deploying one exporter per Redis node, listening on redis_exporter_port 9121 by default. It scrapes metrics from all Redis instances on the node.
When set to false, roles/redis/tasks/exporter.yml still renders config files but skips starting the redis_exporter systemd service (the redis_exporter_launch task has when: redis_exporter_enabled|bool), allowing manually configured exporters to remain.
redis_exporter_port
Parameter: redis_exporter_port, Type: port, Level: C
Redis Exporter listen port, default value: 9121
redis_exporter_options
Parameter: redis_exporter_options, Type: string, Level: C/I
Extra CLI arguments for Redis Exporter, rendered to /etc/default/redis_exporter (see roles/redis/tasks/exporter.yml), default is empty string. REDIS_EXPORTER_OPTS is appended to the systemd service’s ExecStart=/bin/redis_exporter $REDIS_EXPORTER_OPTS, useful for configuring extra scrape targets or filtering behavior.
redis_mode
Parameter: redis_mode, Type: enum, Level: C
Redis cluster operating mode, three options: standalone, cluster, sentinel. Default: standalone
standalone: Default, independent Redis master-slave modecluster: Redis native cluster modesentinel: Redis high availability component: Sentinel
When using standalone mode, Pigsty sets up Redis replication based on the replica_of parameter.
When using cluster mode, Pigsty creates a native Redis cluster using all defined instances based on the redis_cluster_replicas parameter.
When redis_mode=sentinel, redis.yml executes the redis-ha phase (lines 80-130 of redis.yml) to distribute targets from redis_sentinel_monitor to all sentinels. When redis_mode=cluster, it also executes the redis-join phase (lines 134-180) calling redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-yes ... --cluster-replicas {{ redis_cluster_replicas }}. Both phases are automatically triggered in normal ./redis.yml -l <cluster> runs, or can be run separately with -t redis-ha or -t redis-join.
redis_conf
Parameter: redis_conf, Type: string, Level: C
Redis config template path, except for Sentinel.
Default: redis.conf, a template file at roles/redis/templates/redis.conf.
To use your own Redis config template, place it in the templates/ directory and set this parameter to the template filename.
Note: Redis Sentinel uses a different template file: roles/redis/templates/redis-sentinel.conf.
redis_bind_address
Parameter: redis_bind_address, Type: ip, Level: C
IP address Redis server binds to. Empty string uses the hostname defined in the inventory.
Default: 0.0.0.0, binding to all available IPv4 addresses on the host.
For security in production environments, bind only to internal IPs by setting this to empty string ''.
When empty, the template roles/redis/templates/redis.conf uses inventory_hostname to render bind <ip>, binding to the management address declared in the inventory.
redis_max_memory
Parameter: redis_max_memory, Type: size, Level: C/I
Maximum memory for each Redis instance, default: 1GB.
redis_mem_policy
Parameter: redis_mem_policy, Type: enum, Level: C
Redis memory eviction policy, default: allkeys-lru
noeviction: Don’t save new values when memory limit is reached; only applies to primary when using replicationallkeys-lru: Keep most recently used keys; remove least recently used (LRU) keysallkeys-lfu: Keep frequently used keys; remove least frequently used (LFU) keysvolatile-lru: Remove least recently used keys with expire field setvolatile-lfu: Remove least frequently used keys with expire field setallkeys-random: Randomly remove keys to make space for new datavolatile-random: Randomly remove keys with expire field setvolatile-ttl: Remove keys with expire field set and shortest remaining TTL
See Redis Eviction Policy for details.
redis_password
Parameter: redis_password, Type: password, Level: C/N
Redis password. Empty string disables password, which is the default behavior.
Note that due to redis_exporter implementation limitations, you can only set one redis_password per node. This is usually not a problem since Pigsty doesn’t allow deploying two different Redis clusters on the same node.
Pigsty automatically writes this password to /etc/default/redis_exporter (REDIS_PASSWORD=...) and uses it in the redis-ha phase with redis-cli -a <password>, so no need to separately configure exporter or Sentinel authentication.
Use a strong password in production environments
redis_rdb_save
Parameter: redis_rdb_save, Type: string[], Level: C
Redis RDB save directives. Use empty list to disable RDB.
Default is ["1200 1"]: dump dataset to disk every 20 minutes if at least 1 key changed.
See Redis Persistence for details.
redis_aof_enabled
Parameter: redis_aof_enabled, Type: bool, Level: C
Enable Redis AOF? Default is false, meaning AOF is not used.
redis_rename_commands
Parameter: redis_rename_commands, Type: dict, Level: C
Rename dangerous Redis commands. A k:v dictionary where old is the command to rename and new is the new name.
Default: {}. You can hide dangerous commands like FLUSHDB and FLUSHALL. Example:
{
"keys": "op_keys",
"flushdb": "op_flushdb",
"flushall": "op_flushall",
"config": "op_config"
}
redis_cluster_replicas
Parameter: redis_cluster_replicas, Type: int, Level: C
Number of replicas per master/primary in Redis native cluster. Default: 1, meaning one replica per master.
redis_sentinel_monitor
Parameter: redis_sentinel_monitor, Type: master[], Level: C
List of masters for Redis Sentinel to monitor, used only on sentinel clusters. Each managed master is defined as:
redis_sentinel_monitor: # primary list for redis sentinel, use cls as name, primary ip:port
- { name: redis-src, host: 10.10.10.45, port: 6379 ,password: redis.src, quorum: 1 }
- { name: redis-dst, host: 10.10.10.48, port: 6379 ,password: redis.dst, quorum: 1 }
name and host are required; port, password, and quorum are optional. quorum sets the number of sentinels needed to agree on master failure, typically more than half of sentinel instances (default is 1).
Starting from Pigsty 4.0, you can add remove: true to an entry, causing the redis-ha phase to only execute SENTINEL REMOVE <name>, useful for cleaning up targets no longer needed.
REDIS_REMOVE
The following parameters are used by the redis_remove role, invoked by the redis-rm.yml playbook, controlling Redis instance removal behavior.
redis_safeguard
Parameter: redis_safeguard, Type: bool, Level: G/C/A
Redis safety guard to prevent accidental removal: when enabled, the redis-rm.yml playbook cannot remove running Redis instances.
Default is false. When set to true, the redis-rm.yml playbook refuses to execute, preventing accidental deletion of running Redis instances.
Override with CLI argument -e redis_safeguard=false to force removal.
redis_rm_data
Parameter: redis_rm_data, Type: bool, Level: G/C/A
Remove Redis data directory when removing Redis instances? Default is true.
The data directory (/data/redis/) contains Redis RDB and AOF files. If not removed, newly deployed Redis instances will load data from these backup files.
Set to false to preserve data directories for later recovery.
redis_rm_pkg
Parameter: redis_rm_pkg, Type: bool, Level: G/C/A
Uninstall Redis and redis_exporter packages when removing Redis instances? Default is false.
Typically not needed to uninstall packages; only enable when completely cleaning up a node.
3 - Playbook
The REDIS module provides two playbooks for deploying/removing Redis clusters/nodes/instances:
redis.yml: Deploy Redis cluster/node/instanceredis-rm.yml: Remove Redis cluster/node/instance
redis.yml
The redis.yml playbook for deploying Redis contains the following subtasks:
redis_node : Init redis node
- redis_install : Install redis & redis_exporter
- redis_user : Create OS user redis
- redis_dir : Configure redis FHS directory structure
redis_exporter : Configure redis_exporter monitoring
- redis_exporter_config : Generate redis_exporter config
- redis_exporter_launch : Launch redis_exporter
redis_instance : Init and restart redis cluster/node/instance
- redis_config : Generate redis instance config
- redis_launch : Launch redis instance
redis_register : Register redis to infrastructure
redis_ha : Configure redis sentinel (sentinel mode only)
redis_join : Join redis native cluster (cluster mode only)
Operation Levels
redis.yml supports three operation levels, controlled by -l to limit target scope and -e redis_port=<port> to specify a single instance:
| Level | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster | -l <cluster> | Deploy all nodes and instances of the entire Redis cluster |
| Node | -l <ip> | Deploy all Redis instances on the specified node |
| Instance | -l <ip> -e redis_port=<port> | Deploy only a single instance on the specified node |
Cluster-Level Operations
Deploy an entire Redis cluster, including all instances on all nodes:
./redis.yml -l redis-ms # deploy the entire redis-ms cluster
./redis.yml -l redis-test # deploy the entire redis-test cluster
./redis.yml -l redis-sentinel # deploy sentinel cluster
Cluster-level operations will:
- Install Redis packages on all nodes
- Create redis user and directory structure on all nodes
- Start redis_exporter on all nodes
- Deploy and start all defined Redis instances
- Register all instances to the monitoring system
- If
sentinelmode, configure sentinel monitoring targets - If
clustermode, form the native cluster
Node-Level Operations
Deploy only all Redis instances on the specified node:
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.10 # deploy all instances on this node
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.11 # deploy another node
Node-level operations are useful for:
- Scaling up by adding new nodes to an existing cluster
- Redeploying all instances on a specific node
- Reinitializing after node failure recovery
Note: Node-level operations do not execute the
redis-haandredis-joinstages. If you need to add a new node to a native cluster, you must manually runredis-cli --cluster add-node
Instance-Level Operations
Use the -e redis_port=<port> parameter to operate on a single instance:
# Deploy only the 6379 port instance on 10.10.10.10
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.10 -e redis_port=6379
# Deploy only the 6380 port instance on 10.10.10.11
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.11 -e redis_port=6380
Instance-level operations are useful for:
- Adding new instances to an existing node
- Redeploying a single failed instance
- Updating a single instance’s configuration
When redis_port is specified:
- Only renders the config file for that port
- Only starts/restarts the systemd service for that port
- Only registers that instance to the monitoring system
- Does not affect other instances on the same node
Common Tags
Use the -t <tag> parameter to selectively execute certain tasks:
# Install packages only, don't start services
./redis.yml -l redis-ms -t redis_node
# Update config and restart instances only
./redis.yml -l redis-ms -t redis_config,redis_launch
# Update monitoring registration only
./redis.yml -l redis-ms -t redis_register
# Configure sentinel monitoring targets only (sentinel mode)
./redis.yml -l redis-sentinel -t redis-ha
# Form native cluster only (cluster mode, auto-runs after first deployment)
./redis.yml -l redis-cluster -t redis-join
Idempotency
redis.yml is idempotent and safe to run repeatedly:
- Repeated execution overwrites existing config files
- Repeated execution restarts Redis instances
- Does not check if instances already exist; directly renders config and restarts
- Suitable for batch updates after configuration changes
Tip: If you only want to update configs without restarting all instances, use
-t redis_configto render configs only, then manually restart the instances you need.
redis-rm.yml
The redis-rm.yml playbook for removing Redis contains the following subtasks:
redis_safeguard : Safety check, abort if redis_safeguard=true
redis_deregister : Remove registration from monitoring system
- rm_metrics : Delete /infra/targets/redis/*.yml
- rm_logs : Revoke /etc/vector/redis.yaml
redis_exporter : Stop and disable redis_exporter
redis : Stop and disable redis instances
redis_data : Delete data directories (when redis_rm_data=true)
redis_pkg : Uninstall packages (when redis_rm_pkg=true)
Operation Levels
redis-rm.yml also supports three operation levels:
| Level | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster | -l <cluster> | Remove all nodes and instances of the entire Redis cluster |
| Node | -l <ip> | Remove all Redis instances on the specified node |
| Instance | -l <ip> -e redis_port=<port> | Remove only a single instance on the specified node |
Cluster-Level Removal
Remove an entire Redis cluster:
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-ms # remove entire redis-ms cluster
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-test # remove entire redis-test cluster
Cluster-level removal will:
- Deregister all instances on all nodes from the monitoring system
- Stop redis_exporter on all nodes
- Stop and disable all Redis instances
- Delete all data directories (if
redis_rm_data=true) - Uninstall packages (if
redis_rm_pkg=true)
Node-Level Removal
Remove only all Redis instances on the specified node:
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.10 # remove all instances on this node
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.11 # remove another node
Node-level removal is useful for:
- Scaling down by removing an entire node
- Cleanup before node decommission
- Preparation before node migration
Node-level removal will:
- Deregister all instances on that node from the monitoring system
- Stop redis_exporter on that node
- Stop all Redis instances on that node
- Delete all data directories on that node
- Delete Vector logging config on that node
Instance-Level Removal
Use the -e redis_port=<port> parameter to remove a single instance:
# Remove only the 6379 port instance on 10.10.10.10
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.10 -e redis_port=6379
# Remove only the 6380 port instance on 10.10.10.11
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.11 -e redis_port=6380
Instance-level removal is useful for:
- Removing a single replica from a node
- Removing instances no longer needed
- Removing the original primary after failover
Behavioral differences when redis_port is specified:
| Component | Node-Level (no redis_port) | Instance-Level (with redis_port) |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring registration | Delete entire node’s registration file | Only remove that instance from registration file |
| redis_exporter | Stop and disable | No operation (other instances still need it) |
| Redis instances | Stop all instances | Only stop the specified port’s instance |
| Data directory | Delete entire /data/redis/ directory | Only delete /data/redis/<cluster>-<node>-<port>/ |
| Vector config | Delete /etc/vector/redis.yaml | No operation (other instances still need it) |
| Packages | Optionally uninstall | No operation |
Control Parameters
redis-rm.yml provides the following control parameters:
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
redis_safeguard | false | Safety guard; when true, refuses to execute removal |
redis_rm_data | true | Whether to delete data directories (RDB/AOF files) |
redis_rm_pkg | false | Whether to uninstall Redis packages |
Usage examples:
# Remove cluster but keep data directories
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-ms -e redis_rm_data=false
# Remove cluster and uninstall packages
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-ms -e redis_rm_pkg=true
# Bypass safeguard to force removal
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-ms -e redis_safeguard=false
Safeguard Mechanism
When a cluster has redis_safeguard: true configured, redis-rm.yml will refuse to execute:
redis-production:
vars:
redis_safeguard: true # enable protection for production
$ ./redis-rm.yml -l redis-production
TASK [ABORT due to redis_safeguard enabled] ***
fatal: [10.10.10.10]: FAILED! => {"msg": "Abort due to redis_safeguard..."}
Explicit override is required to execute:
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-production -e redis_safeguard=false
Quick Reference
Deployment Quick Reference
# Deploy entire cluster
./redis.yml -l <cluster>
# Scale up: deploy new node
./redis.yml -l <new-node-ip>
# Scale up: add new instance to existing node (add definition to config first)
./redis.yml -l <ip> -e redis_port=<new-port>
# Update config and restart
./redis.yml -l <cluster> -t redis_config,redis_launch
# Update single instance config only
./redis.yml -l <ip> -e redis_port=<port> -t redis_config,redis_launch
Removal Quick Reference
# Remove entire cluster
./redis-rm.yml -l <cluster>
# Scale down: remove entire node
./redis-rm.yml -l <ip>
# Scale down: remove single instance
./redis-rm.yml -l <ip> -e redis_port=<port>
# Remove but keep data
./redis-rm.yml -l <cluster> -e redis_rm_data=false
# Complete cleanup (including packages)
./redis-rm.yml -l <cluster> -e redis_rm_pkg=true
Wrapper Scripts
Pigsty provides convenient wrapper scripts:
# Deploy
bin/redis-add <cluster> # deploy cluster
bin/redis-add <ip> # deploy node
bin/redis-add <ip> <port> # deploy instance
# Remove
bin/redis-rm <cluster> # remove cluster
bin/redis-rm <ip> # remove node
bin/redis-rm <ip> <port> # remove instance
Demo
Initialize Redis cluster with Redis playbook:
4 - Administration
Here are some common Redis administration task SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures):
Basic Operations
High Availability
Scaling & Migration
Troubleshooting
For more questions, please refer to FAQ: REDIS.
Initialize Redis
You can use the redis.yml playbook to initialize Redis clusters, nodes, or instances:
# Initialize all Redis instances in the cluster
./redis.yml -l <cluster> # init redis cluster
# Initialize all Redis instances on a specific node
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.10 # init redis node
# Initialize a specific Redis instance: 10.10.10.11:6379
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.11 -e redis_port=6379 -t redis
You can also use wrapper scripts to initialize:
bin/redis-add redis-ms # create redis cluster 'redis-ms'
bin/redis-add 10.10.10.10 # create redis node '10.10.10.10'
bin/redis-add 10.10.10.10 6379 # create redis instance '10.10.10.10:6379'
Remove Redis
You can use the redis-rm.yml playbook to remove Redis clusters, nodes, or instances:
# Remove Redis cluster `redis-test`
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-test
# Remove Redis cluster `redis-test` and uninstall Redis packages
./redis-rm.yml -l redis-test -e redis_rm_pkg=true
# Remove all instances on Redis node 10.10.10.13
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.13
# Remove a specific Redis instance 10.10.10.13:6379
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.13 -e redis_port=6379
You can also use wrapper scripts to remove Redis clusters/nodes/instances:
bin/redis-rm redis-ms # remove redis cluster 'redis-ms'
bin/redis-rm 10.10.10.10 # remove redis node '10.10.10.10'
bin/redis-rm 10.10.10.10 6379 # remove redis instance '10.10.10.10:6379'
Reconfigure Redis
You can partially run the redis.yml playbook to reconfigure Redis clusters, nodes, or instances:
./redis.yml -l <cluster> -t redis_config,redis_launch
Note that Redis cannot reload configuration online. You must restart Redis using the launch task to make configuration changes take effect.
Using Redis Client
Access Redis instances with redis-cli:
$ redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 # <--- connect with host and port
10.10.10.10:6379> auth redis.ms # <--- authenticate with password
OK
10.10.10.10:6379> set a 10 # <--- set a key
OK
10.10.10.10:6379> get a # <--- get the key value
"10"
Redis provides the redis-benchmark tool, which can be used for Redis performance evaluation or to generate load for testing.
redis-benchmark -h 10.10.10.13 -p 6379
Configure Redis Replica
https://redis.io/commands/replicaof/
# Promote a Redis instance to primary
> REPLICAOF NO ONE
"OK"
# Make a Redis instance a replica of another instance
> REPLICAOF 127.0.0.1 6799
"OK"
Configure HA with Sentinel
Redis standalone master-slave clusters can be configured for automatic high availability through Redis Sentinel. For detailed information, please refer to the Sentinel official documentation.
Using the four-node sandbox environment as an example, a Redis Sentinel cluster redis-meta can be used to manage multiple standalone Redis master-slave clusters.
Taking the one-master-one-slave Redis standalone cluster redis-ms as an example, you need to add the target on each Sentinel instance using SENTINEL MONITOR and provide the password using SENTINEL SET, and the high availability is configured.
# For each sentinel, add the redis master to sentinel management: (26379,26380,26381)
$ redis-cli -h 10.10.10.11 -p 26379 -a redis.meta
10.10.10.11:26379> SENTINEL MONITOR redis-ms 10.10.10.10 6379 1
10.10.10.11:26379> SENTINEL SET redis-ms auth-pass redis.ms # if auth enabled, password needs to be configured
If you want to remove a Redis master-slave cluster managed by Sentinel, use SENTINEL REMOVE <name>.
You can use the redis_sentinel_monitor parameter defined on the Sentinel cluster to automatically configure the list of masters managed by Sentinel.
redis_sentinel_monitor: # list of masters to be monitored, port, password, quorum (should be more than 1/2 of sentinels) are optional
- { name: redis-src, host: 10.10.10.45, port: 6379 ,password: redis.src, quorum: 1 }
- { name: redis-dst, host: 10.10.10.48, port: 6379 ,password: redis.dst, quorum: 1 }
The redis-ha stage in redis.yml will render /tmp/<cluster>.monitor on each sentinel instance based on this list and execute SENTINEL REMOVE and SENTINEL MONITOR commands sequentially, ensuring the sentinel management state remains consistent with the inventory. If you only want to remove a target without re-adding it, set remove: true on the monitor object, and the playbook will skip re-registration after SENTINEL REMOVE.
Use the following command to refresh the managed master list on the Redis Sentinel cluster:
./redis.yml -l redis-meta -t redis-ha # replace redis-meta if your Sentinel cluster has a different name
Initialize Redis Native Cluster
When redis_mode is set to cluster, redis.yml will additionally execute the redis-join stage: it uses redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-yes ... --cluster-replicas {{ redis_cluster_replicas }} in /tmp/<cluster>-join.sh to join all instances into a native cluster.
This step runs automatically during the first deployment. Subsequently re-running ./redis.yml -l <cluster> -t redis-join will regenerate and execute the same command. Since --cluster create is not idempotent, you should only trigger this stage separately when you are sure you need to rebuild the entire native cluster.
Scale Up Redis Nodes
Scale Up Standalone Cluster
When adding new nodes/instances to an existing Redis master-slave cluster, first add the new definition in the inventory:
redis-ms:
hosts:
10.10.10.10: { redis_node: 1 , redis_instances: { 6379: { }, 6380: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } }
10.10.10.11: { redis_node: 2 , redis_instances: { 6379: { replica_of: '10.10.10.10 6379' } } } # new node
vars: { redis_cluster: redis-ms ,redis_password: 'redis.ms' ,redis_max_memory: 64MB }
Then deploy only the new node:
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.11 # deploy only the new node
Scale Up Native Cluster
Adding new nodes to a Redis native cluster requires additional steps:
# 1. Add the new node definition in the inventory
# 2. Deploy the new node
./redis.yml -l 10.10.10.14
# 3. Add the new node to the cluster (manual execution)
redis-cli --cluster add-node 10.10.10.14:6379 10.10.10.12:6379
# 4. Reshard slots if needed
redis-cli --cluster reshard 10.10.10.12:6379
Scale Up Sentinel Cluster
To add new instances to a Sentinel cluster:
# Add new sentinel instances in the inventory, then execute:
./redis.yml -l <sentinel-cluster> -t redis_instance
Scale Down Redis Nodes
Scale Down Standalone Cluster
# 1. If removing a replica, just remove it directly
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.11 -e redis_port=6379
# 2. If removing the primary, first perform a failover
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6380 REPLICAOF NO ONE # promote replica
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 REPLICAOF 10.10.10.10 6380 # demote original primary
# 3. Then remove the original primary
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.10 -e redis_port=6379
# 4. Update the inventory to remove the definition
Scale Down Native Cluster
# 1. First migrate data slots
redis-cli --cluster reshard 10.10.10.12:6379 \
--cluster-from <node-id> --cluster-to <target-node-id> --cluster-slots <count>
# 2. Remove node from cluster
redis-cli --cluster del-node 10.10.10.12:6379 <node-id>
# 3. Remove the instance
./redis-rm.yml -l 10.10.10.14
# 4. Update the inventory
Backup and Restore
Manual Backup
# Trigger RDB snapshot
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 -a <password> BGSAVE
# Check snapshot status
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 -a <password> LASTSAVE
# Copy RDB file (default location)
cp /data/redis/redis-ms-1-6379/dump.rdb /backup/redis-ms-$(date +%Y%m%d).rdb
Data Restore
# 1. Stop Redis instance
sudo systemctl stop redis-ms-1-6379
# 2. Replace RDB file
cp /backup/redis-ms-20241231.rdb /data/redis/redis-ms-1-6379/dump.rdb
chown redis:redis /data/redis/redis-ms-1-6379/dump.rdb
# 3. Start Redis instance
sudo systemctl start redis-ms-1-6379
Using AOF Persistence
If you need higher data safety, enable AOF:
redis-ms:
vars:
redis_aof_enabled: true
redis_rdb_save: ['900 1', '300 10', '60 10000'] # keep RDB as well
Redeploy to apply AOF configuration:
./redis.yml -l redis-ms -t redis_config,redis_launch
Common Issue Diagnosis
Connection Troubleshooting
# Check Redis service status
systemctl status redis-ms-1-6379
# Check port listening
ss -tlnp | grep 6379
# Check firewall
sudo iptables -L -n | grep 6379
# Test connection
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 PING
Memory Troubleshooting
# Check memory usage
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 INFO memory
# Find big keys
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 --bigkeys
# Memory analysis report
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 MEMORY DOCTOR
Performance Troubleshooting
# Check slow query log
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 SLOWLOG GET 10
# Real-time command monitoring
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 MONITOR
# Check client connections
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 CLIENT LIST
Replication Troubleshooting
# Check replication status
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6379 INFO replication
# Check replication lag
redis-cli -h 10.10.10.10 -p 6380 INFO replication | grep lag
Performance Tuning
Memory Optimization
redis-cache:
vars:
redis_max_memory: 4GB # set based on available memory
redis_mem_policy: allkeys-lru # LRU recommended for cache scenarios
redis_conf: redis.conf
Persistence Optimization
# Pure cache scenario: disable persistence
redis-cache:
vars:
redis_rdb_save: [] # disable RDB
redis_aof_enabled: false # disable AOF
# Data safety scenario: enable both RDB and AOF
redis-data:
vars:
redis_rdb_save: ['900 1', '300 10', '60 10000']
redis_aof_enabled: true
Connection Pool Recommendations
When connecting to Redis from client applications:
- Use connection pooling to avoid frequent connection creation
- Set reasonable timeout values (recommended 1-3 seconds)
- Enable TCP keepalive
- For high-concurrency scenarios, consider using Pipeline for batch operations
Key Monitoring Metrics
Monitor these metrics through Grafana dashboards:
- Memory usage: Pay attention when
redis:ins:mem_usage> 80% - CPU usage: Pay attention when
redis:ins:cpu_usage> 70% - QPS: Watch for spikes and abnormal fluctuations
- Response time: Investigate when
redis:ins:rt> 1ms - Connection count: Monitor connection growth trends
- Replication lag: Important for master-slave replication scenarios
5 - Monitoring
Dashboards
The REDIS module provides 3 monitoring dashboards:
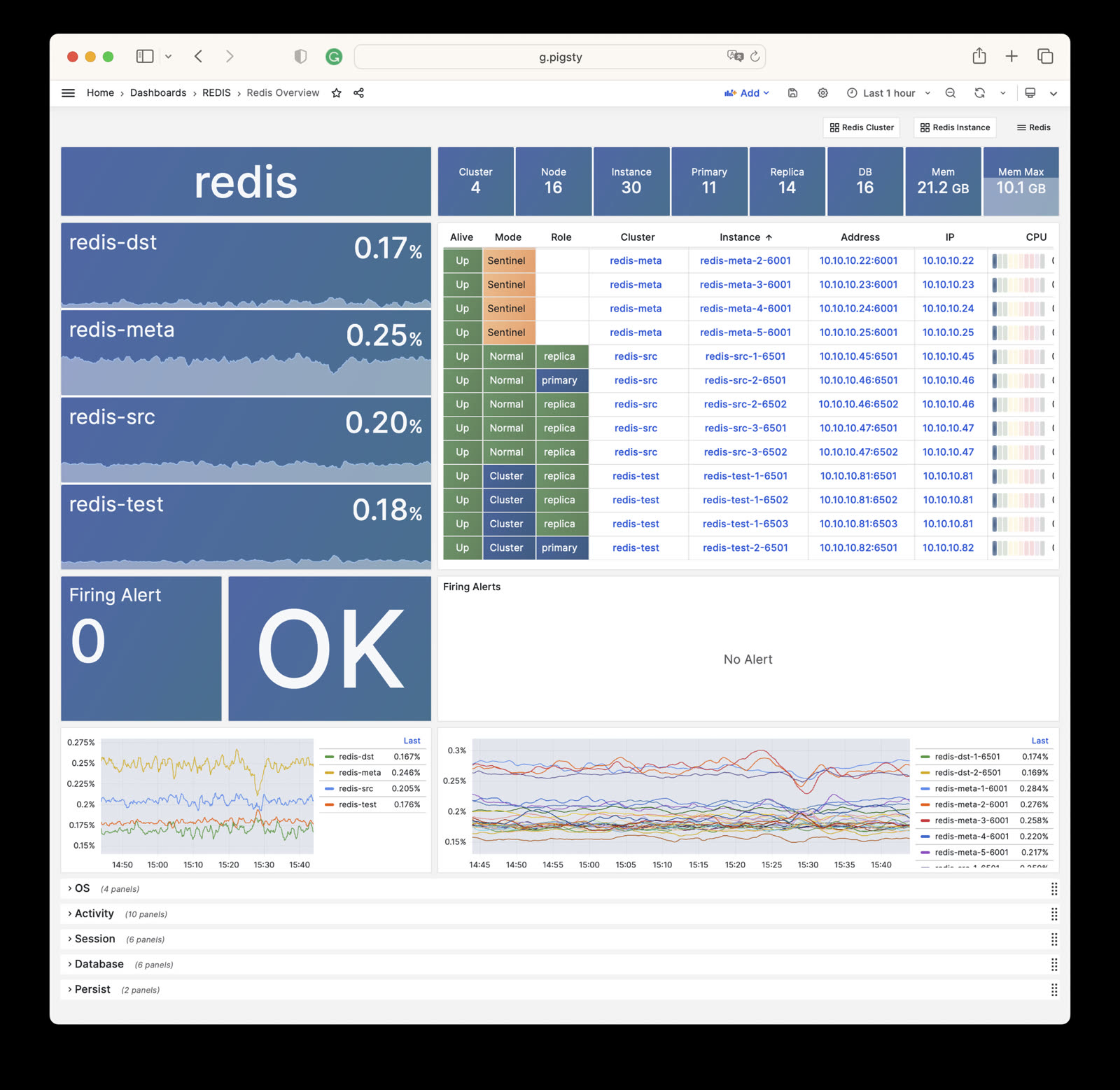
- Redis Overview: Overview of all Redis clusters
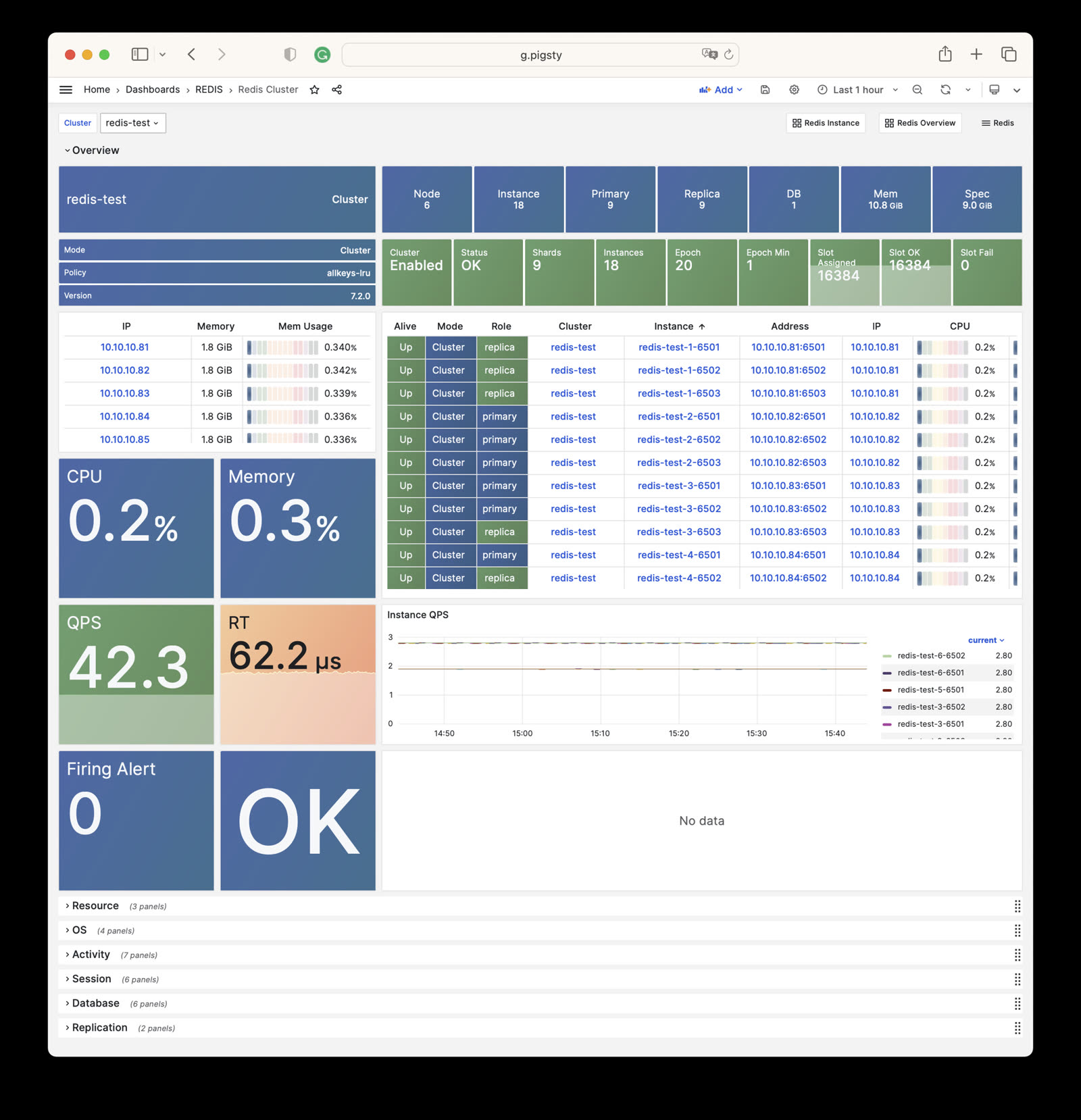
- Redis Cluster: Details of a single Redis cluster
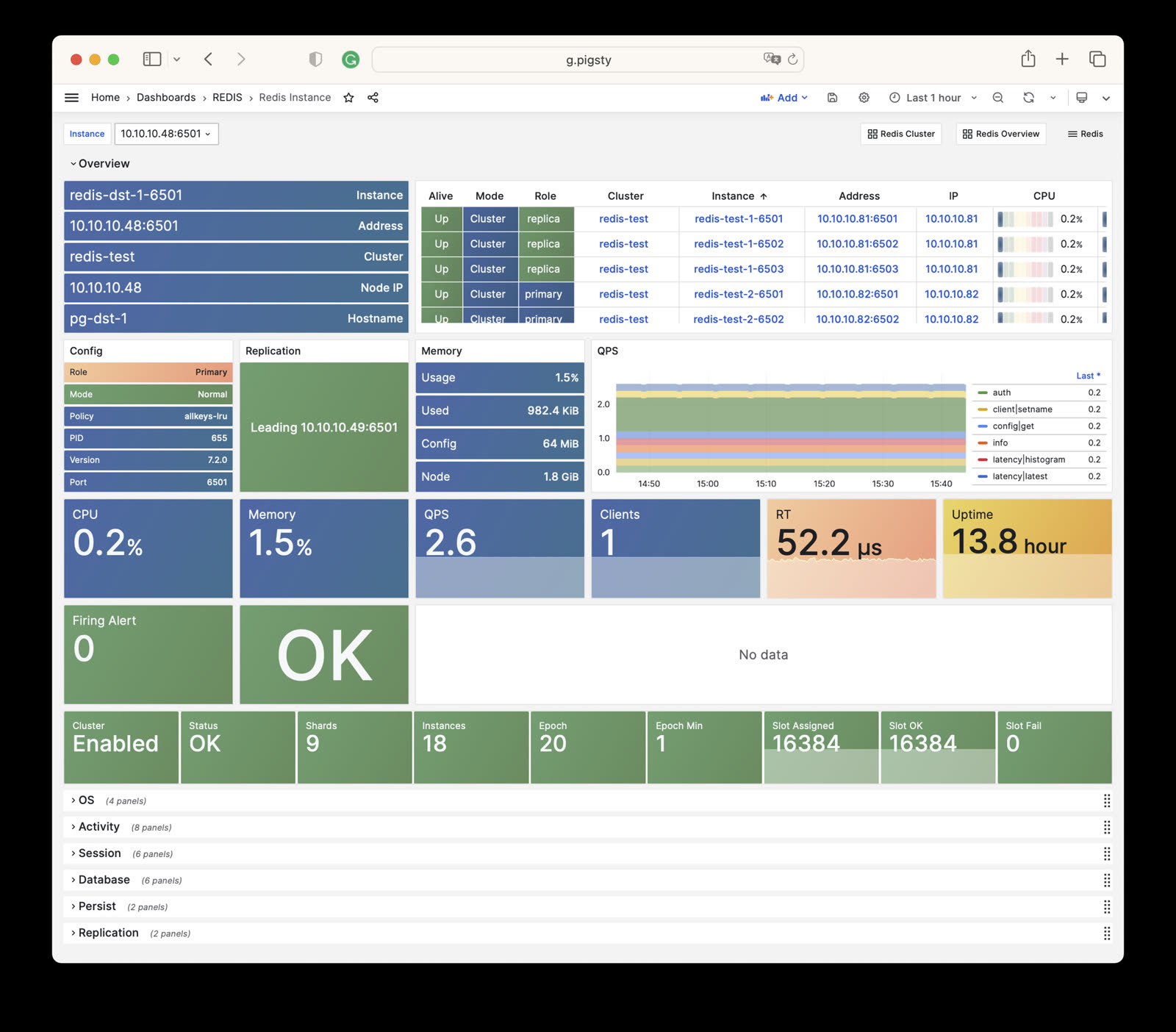
- Redis Instance: Details of a single Redis instance
Monitoring
Pigsty provides three monitoring dashboards for the REDIS module:
Redis Overview
Redis Overview: Overview of all Redis clusters/instances
Redis Cluster
Redis Cluster: Details of a single Redis cluster
Redis Instance
Redis Instance: Details of a single Redis instance
Alert Rules
Pigsty provides the following six predefined alert rules for Redis, defined in files/victoria/rules/redis.yml:
RedisDown: Redis instance is downRedisRejectConn: Redis instance rejecting connectionsRedisRTHigh: Redis instance response time is too highRedisCPUHigh: Redis instance CPU usage is too highRedisMemHigh: Redis instance memory usage is too highRedisQPSHigh: Redis instance QPS is too high
#==============================================================#
# Error #
#==============================================================#
# redis down triggers a P0 alert
- alert: RedisDown
expr: redis_up < 1
for: 1m
labels: { level: 0, severity: CRIT, category: redis }
annotations:
summary: "CRIT RedisDown: {{ $labels.ins }} {{ $labels.instance }} {{ $value }}"
description: |
redis_up[ins={{ $labels.ins }}, instance={{ $labels.instance }}] = {{ $value }} == 0
http://g.pigsty/d/redis-instance?from=now-5m&to=now&var-ins={{$labels.ins}}
# redis reject connection in last 5m
- alert: RedisRejectConn
expr: redis:ins:conn_reject > 0
labels: { level: 0, severity: CRIT, category: redis }
annotations:
summary: "CRIT RedisRejectConn: {{ $labels.ins }} {{ $labels.instance }} {{ $value }}"
description: |
redis:ins:conn_reject[cls={{ $labels.cls }}, ins={{ $labels.ins }}][5m] = {{ $value }} > 0
http://g.pigsty/d/redis-instance?from=now-10m&to=now&viewPanel=88&fullscreen&var-ins={{ $labels.ins }}
#==============================================================#
# Latency #
#==============================================================#
# redis avg query response time > 160 µs
- alert: RedisRTHigh
expr: redis:ins:rt > 0.00016
for: 1m
labels: { level: 1, severity: WARN, category: redis }
annotations:
summary: "WARN RedisRTHigh: {{ $labels.cls }} {{ $labels.ins }}"
description: |
pg:ins:query_rt[cls={{ $labels.cls }}, ins={{ $labels.ins }}] = {{ $value }} > 160µs
http://g.pigsty/d/redis-instance?from=now-10m&to=now&viewPanel=97&fullscreen&var-ins={{ $labels.ins }}
#==============================================================#
# Saturation #
#==============================================================#
# redis cpu usage more than 70% for 1m
- alert: RedisCPUHigh
expr: redis:ins:cpu_usage > 0.70
for: 1m
labels: { level: 1, severity: WARN, category: redis }
annotations:
summary: "WARN RedisCPUHigh: {{ $labels.cls }} {{ $labels.ins }}"
description: |
redis:ins:cpu_all[cls={{ $labels.cls }}, ins={{ $labels.ins }}] = {{ $value }} > 60%
http://g.pigsty/d/redis-instance?from=now-10m&to=now&viewPanel=43&fullscreen&var-ins={{ $labels.ins }}
# redis mem usage more than 70% for 1m
- alert: RedisMemHigh
expr: redis:ins:mem_usage > 0.70
for: 1m
labels: { level: 1, severity: WARN, category: redis }
annotations:
summary: "WARN RedisMemHigh: {{ $labels.cls }} {{ $labels.ins }}"
description: |
redis:ins:mem_usage[cls={{ $labels.cls }}, ins={{ $labels.ins }}] = {{ $value }} > 80%
http://g.pigsty/d/redis-instance?from=now-10m&to=now&viewPanel=7&fullscreen&var-ins={{ $labels.ins }}
#==============================================================#
# Traffic #
#==============================================================#
# redis qps more than 32000 for 5m
- alert: RedisQPSHigh
expr: redis:ins:qps > 32000
for: 5m
labels: { level: 2, severity: INFO, category: redis }
annotations:
summary: "INFO RedisQPSHigh: {{ $labels.cls }} {{ $labels.ins }}"
description: |
redis:ins:qps[cls={{ $labels.cls }}, ins={{ $labels.ins }}] = {{ $value }} > 16000
http://g.pigsty/d/redis-instance?from=now-10m&to=now&viewPanel=96&fullscreen&var-ins={{ $labels.ins }}
6 - Metrics
The REDIS module contains 275 available monitoring metrics.
| Metric Name | Type | Labels | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALERTS | Unknown | cls, ip, level, severity, instance, category, ins, alertname, job, alertstate | N/A |
| ALERTS_FOR_STATE | Unknown | cls, ip, level, severity, instance, category, ins, alertname, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:aof_rewrite_time | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:blocked_clients | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:clients | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cmd_qps | Unknown | cls, cmd, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cmd_rt | Unknown | cls, cmd, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cmd_time | Unknown | cls, cmd, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:conn_rate | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:conn_reject | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cpu_sys | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cpu_sys_child | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cpu_usage | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cpu_usage_child | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cpu_user | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:cpu_user_child | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:fork_time | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:key_evict | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:key_expire | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:key_hit | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:key_hit_rate | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:key_miss | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:mem_max | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:mem_usage | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:mem_usage_max | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:mem_used | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:net_traffic | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:qps | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:qps_mu | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:qps_realtime | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:qps_sigma | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:rt | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:rt_mu | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:rt_sigma | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:rx | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:size | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:cls:tx | Unknown | cls, job | N/A |
| redis:env:blocked_clients | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:clients | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:cmd_qps | Unknown | cmd, job | N/A |
| redis:env:cmd_rt | Unknown | cmd, job | N/A |
| redis:env:cmd_time | Unknown | cmd, job | N/A |
| redis:env:conn_rate | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:conn_reject | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:cpu_usage | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:cpu_usage_child | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:key_evict | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:key_expire | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:key_hit | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:key_hit_rate | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:key_miss | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:mem_usage | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:net_traffic | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:qps | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:qps_mu | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:qps_realtime | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:qps_sigma | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:rt | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:rt_mu | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:rt_sigma | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:rx | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:env:tx | Unknown | job | N/A |
| redis:ins | Unknown | cls, id, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:blocked_clients | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:clients | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cmd_qps | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cmd_rt | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cmd_time | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:conn_rate | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:conn_reject | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cpu_sys | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cpu_sys_child | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cpu_usage | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cpu_usage_child | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cpu_user | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:cpu_user_child | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:key_evict | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:key_expire | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:key_hit | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:key_hit_rate | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:key_miss | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:lsn_rate | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:mem_usage | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:net_traffic | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:qps | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:qps_mu | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:qps_realtime | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:qps_sigma | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:rt | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:rt_mu | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:rt_sigma | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:rx | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:ins:tx | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:node:ip | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis:node:mem_alloc | Unknown | cls, ip, job | N/A |
| redis:node:mem_total | Unknown | cls, ip, job | N/A |
| redis:node:mem_used | Unknown | cls, ip, job | N/A |
| redis:node:qps | Unknown | cls, ip, job | N/A |
| redis_active_defrag_running | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | active_defrag_running metric |
| redis_allocator_active_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_active_bytes metric |
| redis_allocator_allocated_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_allocated_bytes metric |
| redis_allocator_frag_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_frag_bytes metric |
| redis_allocator_frag_ratio | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_frag_ratio metric |
| redis_allocator_resident_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_resident_bytes metric |
| redis_allocator_rss_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_rss_bytes metric |
| redis_allocator_rss_ratio | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | allocator_rss_ratio metric |
| redis_aof_current_rewrite_duration_sec | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_current_rewrite_duration_sec metric |
| redis_aof_enabled | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_enabled metric |
| redis_aof_last_bgrewrite_status | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_last_bgrewrite_status metric |
| redis_aof_last_cow_size_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_last_cow_size_bytes metric |
| redis_aof_last_rewrite_duration_sec | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_last_rewrite_duration_sec metric |
| redis_aof_last_write_status | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_last_write_status metric |
| redis_aof_rewrite_in_progress | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_rewrite_in_progress metric |
| redis_aof_rewrite_scheduled | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | aof_rewrite_scheduled metric |
| redis_blocked_clients | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | blocked_clients metric |
| redis_client_recent_max_input_buffer_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | client_recent_max_input_buffer_bytes metric |
| redis_client_recent_max_output_buffer_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | client_recent_max_output_buffer_bytes metric |
| redis_clients_in_timeout_table | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | clients_in_timeout_table metric |
| redis_cluster_connections | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_connections metric |
| redis_cluster_current_epoch | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_current_epoch metric |
| redis_cluster_enabled | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_enabled metric |
| redis_cluster_known_nodes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_known_nodes metric |
| redis_cluster_messages_received_total | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_messages_received_total metric |
| redis_cluster_messages_sent_total | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_messages_sent_total metric |
| redis_cluster_my_epoch | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_my_epoch metric |
| redis_cluster_size | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_size metric |
| redis_cluster_slots_assigned | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_slots_assigned metric |
| redis_cluster_slots_fail | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_slots_fail metric |
| redis_cluster_slots_ok | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_slots_ok metric |
| redis_cluster_slots_pfail | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_slots_pfail metric |
| redis_cluster_state | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_state metric |
| redis_cluster_stats_messages_meet_received | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_stats_messages_meet_received metric |
| redis_cluster_stats_messages_meet_sent | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_stats_messages_meet_sent metric |
| redis_cluster_stats_messages_ping_received | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_stats_messages_ping_received metric |
| redis_cluster_stats_messages_ping_sent | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_stats_messages_ping_sent metric |
| redis_cluster_stats_messages_pong_received | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_stats_messages_pong_received metric |
| redis_cluster_stats_messages_pong_sent | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cluster_stats_messages_pong_sent metric |
| redis_commands_duration_seconds_total | counter | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | Total amount of time in seconds spent per command |
| redis_commands_failed_calls_total | counter | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | Total number of errors prior command execution per command |
| redis_commands_latencies_usec_bucket | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, le, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_commands_latencies_usec_count | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_commands_latencies_usec_sum | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_commands_processed_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | commands_processed_total metric |
| redis_commands_rejected_calls_total | counter | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | Total number of errors within command execution per command |
| redis_commands_total | counter | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | Total number of calls per command |
| redis_config_io_threads | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | config_io_threads metric |
| redis_config_maxclients | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | config_maxclients metric |
| redis_config_maxmemory | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | config_maxmemory metric |
| redis_connected_clients | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | connected_clients metric |
| redis_connected_slave_lag_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, slave_ip, instance, slave_state, ins, slave_port, job | Lag of connected slave |
| redis_connected_slave_offset_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, slave_ip, instance, slave_state, ins, slave_port, job | Offset of connected slave |
| redis_connected_slaves | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | connected_slaves metric |
| redis_connections_received_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | connections_received_total metric |
| redis_cpu_sys_children_seconds_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cpu_sys_children_seconds_total metric |
| redis_cpu_sys_main_thread_seconds_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cpu_sys_main_thread_seconds_total metric |
| redis_cpu_sys_seconds_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cpu_sys_seconds_total metric |
| redis_cpu_user_children_seconds_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cpu_user_children_seconds_total metric |
| redis_cpu_user_main_thread_seconds_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cpu_user_main_thread_seconds_total metric |
| redis_cpu_user_seconds_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | cpu_user_seconds_total metric |
| redis_db_keys | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, db, job | Total number of keys by DB |
| redis_db_keys_expiring | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, db, job | Total number of expiring keys by DB |
| redis_defrag_hits | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | defrag_hits metric |
| redis_defrag_key_hits | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | defrag_key_hits metric |
| redis_defrag_key_misses | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | defrag_key_misses metric |
| redis_defrag_misses | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | defrag_misses metric |
| redis_dump_payload_sanitizations | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | dump_payload_sanitizations metric |
| redis_errors_total | counter | cls, ip, err, instance, ins, job | Total number of errors per error type |
| redis_evicted_keys_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | evicted_keys_total metric |
| redis_expired_keys_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | expired_keys_total metric |
| redis_expired_stale_percentage | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | expired_stale_percentage metric |
| redis_expired_time_cap_reached_total | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | expired_time_cap_reached_total metric |
| redis_exporter_build_info | gauge | cls, golang_version, ip, commit_sha, instance, version, ins, job, build_date | redis exporter build_info |
| redis_exporter_last_scrape_connect_time_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | exporter_last_scrape_connect_time_seconds metric |
| redis_exporter_last_scrape_duration_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | exporter_last_scrape_duration_seconds metric |
| redis_exporter_last_scrape_error | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | The last scrape error status. |
| redis_exporter_scrape_duration_seconds_count | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_exporter_scrape_duration_seconds_sum | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_exporter_scrapes_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Current total redis scrapes. |
| redis_instance_info | gauge | cls, ip, os, role, instance, run_id, redis_version, tcp_port, process_id, ins, redis_mode, maxmemory_policy, redis_build_id, job | Information about the Redis instance |
| redis_io_threaded_reads_processed | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | io_threaded_reads_processed metric |
| redis_io_threaded_writes_processed | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | io_threaded_writes_processed metric |
| redis_io_threads_active | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | io_threads_active metric |
| redis_keyspace_hits_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | keyspace_hits_total metric |
| redis_keyspace_misses_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | keyspace_misses_total metric |
| redis_last_key_groups_scrape_duration_milliseconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Duration of the last key group metrics scrape in milliseconds |
| redis_last_slow_execution_duration_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | The amount of time needed for last slow execution, in seconds |
| redis_latency_percentiles_usec | summary | cls, cmd, ip, instance, quantile, ins, job | A summary of latency percentile distribution per command |
| redis_latency_percentiles_usec_count | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_latency_percentiles_usec_sum | Unknown | cls, cmd, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| redis_latest_fork_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | latest_fork_seconds metric |
| redis_lazyfree_pending_objects | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | lazyfree_pending_objects metric |
| redis_loading_dump_file | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | loading_dump_file metric |
| redis_master_last_io_seconds_ago | gauge | cls, ip, master_host, instance, ins, job, master_port | Master last io seconds ago |
| redis_master_link_up | gauge | cls, ip, master_host, instance, ins, job, master_port | Master link status on Redis slave |
| redis_master_repl_offset | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | master_repl_offset metric |
| redis_master_sync_in_progress | gauge | cls, ip, master_host, instance, ins, job, master_port | Master sync in progress |
| redis_mem_clients_normal | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | mem_clients_normal metric |
| redis_mem_clients_slaves | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | mem_clients_slaves metric |
| redis_mem_fragmentation_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | mem_fragmentation_bytes metric |
| redis_mem_fragmentation_ratio | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | mem_fragmentation_ratio metric |
| redis_mem_not_counted_for_eviction_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | mem_not_counted_for_eviction_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_max_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_max_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_dataset_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_dataset_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_lua_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_lua_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_overhead_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_overhead_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_peak_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_peak_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_rss_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_rss_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_scripts_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_scripts_bytes metric |
| redis_memory_used_startup_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | memory_used_startup_bytes metric |
| redis_migrate_cached_sockets_total | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | migrate_cached_sockets_total metric |
| redis_module_fork_in_progress | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | module_fork_in_progress metric |
| redis_module_fork_last_cow_size | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | module_fork_last_cow_size metric |
| redis_net_input_bytes_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | net_input_bytes_total metric |
| redis_net_output_bytes_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | net_output_bytes_total metric |
| redis_number_of_cached_scripts | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | number_of_cached_scripts metric |
| redis_process_id | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | process_id metric |
| redis_pubsub_channels | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | pubsub_channels metric |
| redis_pubsub_patterns | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | pubsub_patterns metric |
| redis_pubsubshard_channels | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | pubsubshard_channels metric |
| redis_rdb_bgsave_in_progress | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_bgsave_in_progress metric |
| redis_rdb_changes_since_last_save | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_changes_since_last_save metric |
| redis_rdb_current_bgsave_duration_sec | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_current_bgsave_duration_sec metric |
| redis_rdb_last_bgsave_duration_sec | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_last_bgsave_duration_sec metric |
| redis_rdb_last_bgsave_status | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_last_bgsave_status metric |
| redis_rdb_last_cow_size_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_last_cow_size_bytes metric |
| redis_rdb_last_save_timestamp_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rdb_last_save_timestamp_seconds metric |
| redis_rejected_connections_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | rejected_connections_total metric |
| redis_repl_backlog_first_byte_offset | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | repl_backlog_first_byte_offset metric |
| redis_repl_backlog_history_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | repl_backlog_history_bytes metric |
| redis_repl_backlog_is_active | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | repl_backlog_is_active metric |
| redis_replica_partial_resync_accepted | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | replica_partial_resync_accepted metric |
| redis_replica_partial_resync_denied | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | replica_partial_resync_denied metric |
| redis_replica_resyncs_full | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | replica_resyncs_full metric |
| redis_replication_backlog_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | replication_backlog_bytes metric |
| redis_second_repl_offset | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | second_repl_offset metric |
| redis_sentinel_master_ckquorum_status | gauge | cls, ip, message, instance, ins, master_name, job | Master ckquorum status |
| redis_sentinel_master_ok_sentinels | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | The number of okay sentinels monitoring this master |
| redis_sentinel_master_ok_slaves | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | The number of okay slaves of the master |
| redis_sentinel_master_sentinels | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | The number of sentinels monitoring this master |
| redis_sentinel_master_setting_ckquorum | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | Show the current ckquorum config for each master |
| redis_sentinel_master_setting_down_after_milliseconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | Show the current down-after-milliseconds config for each master |
| redis_sentinel_master_setting_failover_timeout | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | Show the current failover-timeout config for each master |
| redis_sentinel_master_setting_parallel_syncs | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | Show the current parallel-syncs config for each master |
| redis_sentinel_master_slaves | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | The number of slaves of the master |
| redis_sentinel_master_status | gauge | cls, ip, master_status, instance, ins, master_address, master_name, job | Master status on Sentinel |
| redis_sentinel_masters | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | The number of masters this sentinel is watching |
| redis_sentinel_running_scripts | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Number of scripts in execution right now |
| redis_sentinel_scripts_queue_length | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Queue of user scripts to execute |
| redis_sentinel_simulate_failure_flags | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Failures simulations |
| redis_sentinel_tilt | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Sentinel is in TILT mode |
| redis_slave_expires_tracked_keys | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | slave_expires_tracked_keys metric |
| redis_slave_info | gauge | cls, ip, master_host, instance, read_only, ins, job, master_port | Information about the Redis slave |
| redis_slave_priority | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | slave_priority metric |
| redis_slave_repl_offset | gauge | cls, ip, master_host, instance, ins, job, master_port | Slave replication offset |
| redis_slowlog_last_id | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Last id of slowlog |
| redis_slowlog_length | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Total slowlog |
| redis_start_time_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Start time of the Redis instance since unix epoch in seconds. |
| redis_target_scrape_request_errors_total | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Errors in requests to the exporter |
| redis_total_error_replies | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | total_error_replies metric |
| redis_total_reads_processed | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | total_reads_processed metric |
| redis_total_system_memory_bytes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | total_system_memory_bytes metric |
| redis_total_writes_processed | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | total_writes_processed metric |
| redis_tracking_clients | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | tracking_clients metric |
| redis_tracking_total_items | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | tracking_total_items metric |
| redis_tracking_total_keys | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | tracking_total_keys metric |
| redis_tracking_total_prefixes | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | tracking_total_prefixes metric |
| redis_unexpected_error_replies | counter | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | unexpected_error_replies metric |
| redis_up | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | Information about the Redis instance |
| redis_uptime_in_seconds | gauge | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | uptime_in_seconds metric |
| scrape_duration_seconds | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| scrape_samples_post_metric_relabeling | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| scrape_samples_scraped | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| scrape_series_added | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
| up | Unknown | cls, ip, instance, ins, job | N/A |
7 - FAQ
ABORT due to redis_safeguard enabled
This means the Redis instance you are trying to remove has the safeguard enabled: this happens when attempting to remove a Redis instance with redis_safeguard set to true. The redis-rm.yml playbook refuses to execute to prevent accidental deletion of running Redis instances.
You can override this protection with the CLI argument -e redis_safeguard=false to force removal of the Redis instance. This is what redis_safeguard is designed for.
How to add a new Redis instance on a node?
Use bin/redis-add <ip> <port> to deploy a new Redis instance on the node.
How to remove a specific instance from a node?
Use bin/redis-rm <ip> <port> to remove a single Redis instance from the node.
Are there plans to upgrade to Valkey or the latest version?
Since Redis is not a core component of this project, there are currently no plans to update to the latest Redis RSAL / AGPLv3 version or Valkey. The Redis version in Pigsty is locked to 7.2.6, the last version using the BSD license.
This version has been validated in large-scale production environments, and Pigsty no longer has such scenarios to re-validate the stability and reliability of newer versions.